Latest News 2025
NOVEMBER 2025
ASN
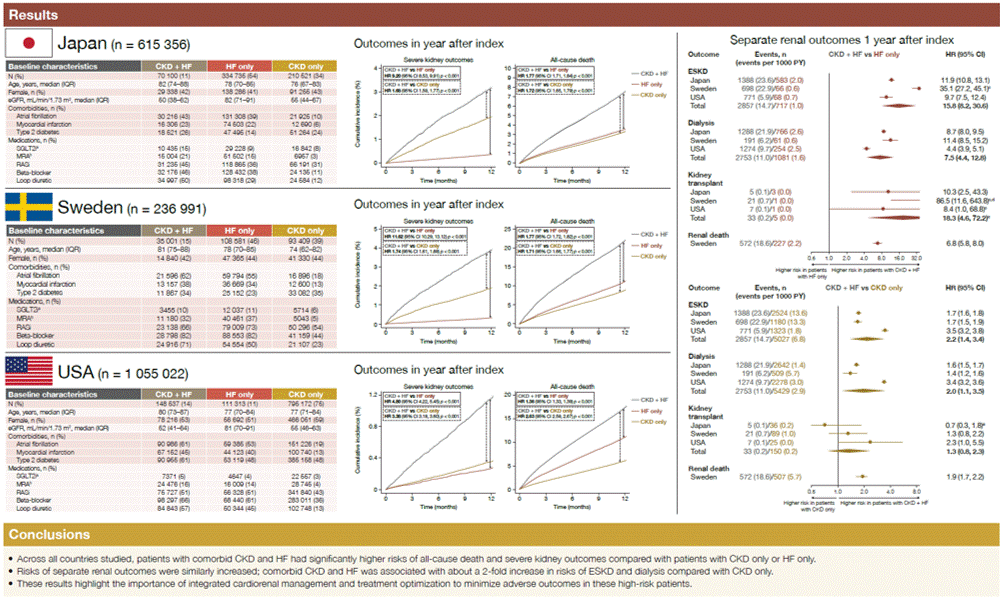
Cardiorenal disease and severe renal outcomes
The CaRe Study
RWE findings from Japan, Sweden, and the USA show that patients with combined CKD and heart failure face a markedly worse kidney prognosis than those with either condition alone. These results underscore the urgent need for improved treatment strategies in cardiorenal disease.
SEPTEMBER 2025
Adv Ther
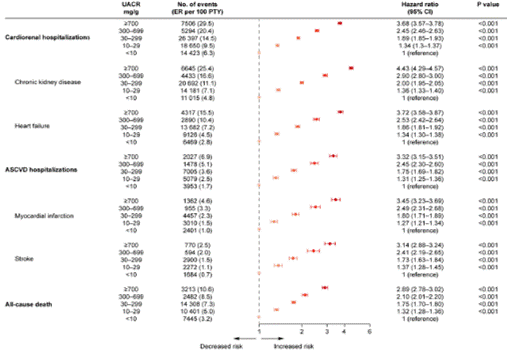
UACR 700 mg/g: CKD progression, cardiorenal risk and SGLT2i effects
The OPTIMISE-CKD Study
RWE from the USA shows that patients with CKD and high-risk proteinuria (UACR ≥ 700 mg/g) experience rapid kidney function decline and markedly higher risks of hospitalization and death. Although SGLT2i provide expected benefits, substantial residual albuminuria highlights the urgent need for improved treatment strategies in this high-risk population.
AUGUST 2025
ESC
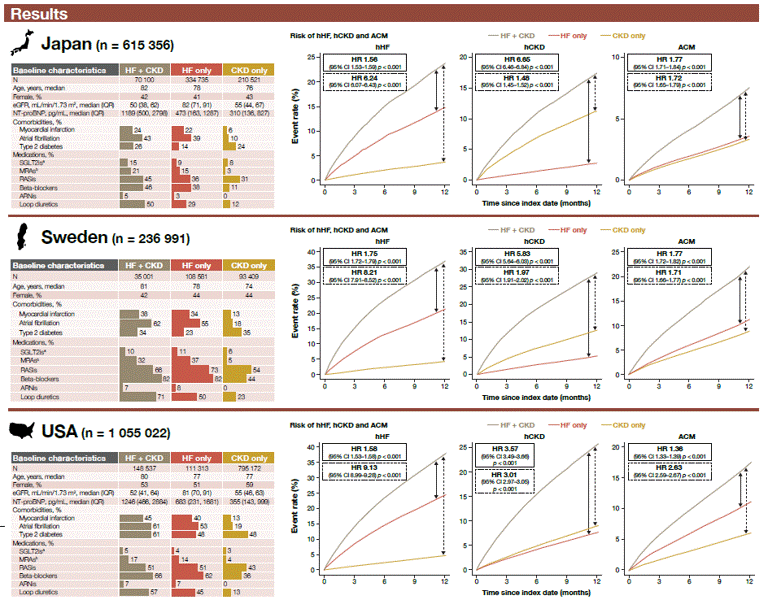
Cardiorenal disease and risks of hospitalizations for HF and CKD
The CaRe Study
RWE from Japan, Sweden and the USA shows that patients with comorbid HF and CKD have substantially higher risks of all-cause death and HF- and CKD-related hospitalizations than patients with either condition alone. These findings underscore the severe prognosis of combined cardiorenal disease and the need for integrated management and optimized GDMT.
AUGUST 2025
ESC
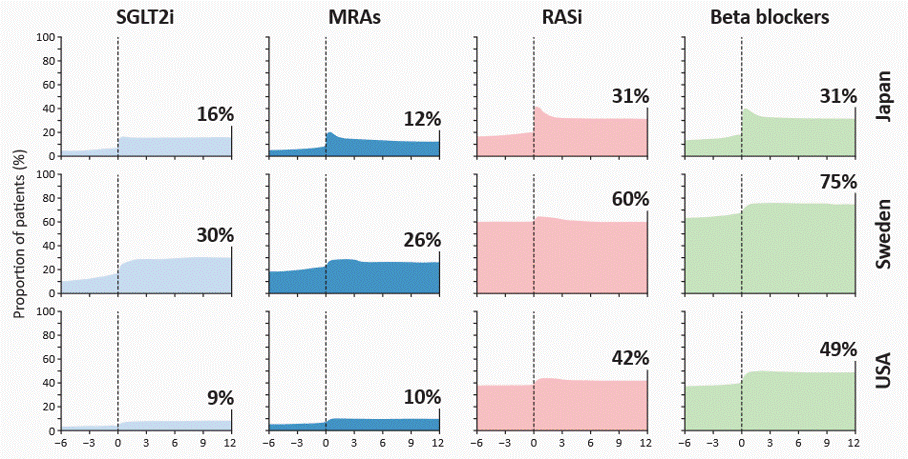
Incident cardiorenal disease and changes in GDMT for HF
The CaRe Study
RWE from Japan, Sweden and the USA shows that patients with incident comorbid HF and CKD have consistently low use of GDMT, both before and after diagnosis. Despite modest increases at the point of incident HF+CKD, substantial GDMT treatment gaps persist, underscoring the urgent need to improve cardiorenal management in this high-risk population.
JULY 2025
BMC Neph
CKD with and without T2D: Risks and GDMT utilization
The OPTIMISE-CKD study
Nationwide RWE from Norway shows that diagnosed CKD is associated with high risks of hospitalization, mortality, and substantial healthcare costs, irrespective of diabetes status. Despite increasing uptake of SGLT2 inhibitors, overall use of kidney-protective therapies remains low—highlighting an urgent need for better GDMT implementation and risk management in CKD.
2 JULY 2025

NICE
Low UACR Restriction for SGLT2i
The OPTIMISE-CKD Study
NICE reversed its prior restriction on dapagliflozin for CKD patients with low UACR (non-T2D, low albuminuria) based on new real-world evidence. This decision reflects growing confidence in high-quality RWE to fill evidence gaps where RCT data are limited.
MAY 2025
NDT
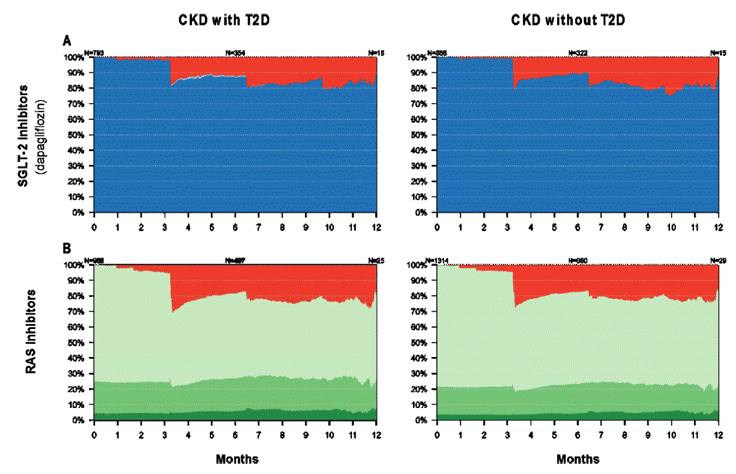
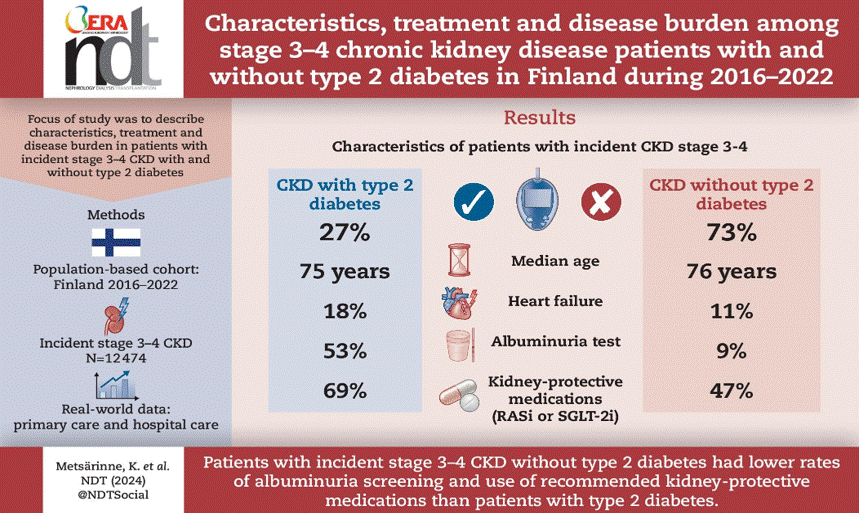
CKD stage 3-4 with or without T2D: UACR, risks and GDMT utilization
The OPTIMISE-CKD Study
RWE from Finland shows that stage 3–4 CKD is highly prevalent, with most patients being non-T2D yet experiencing similarly high risks of hospitalization and death. Albuminuria testing and use of kidney-protective therapies were low—especially in non-T2D patients—highlighting an urgent need for improved CKD detection and preventive treatment.
17 MAY 2025
ESC HF
Cardiorenal Disease Pathways - The CaRe Study
This study is the first to describe the distinct cardiorenal disease pathways leading to comorbid HF+CKD, showing whether patients progress HF→CKD, CKD→HF, or present simultaneously. Across all pathways,we show major gaps in GDMT use and limited nephrology involvement, underscoring the need for earlier detection and integrated cardiorenal care.
12 FEBRUARY 2025
EHJ
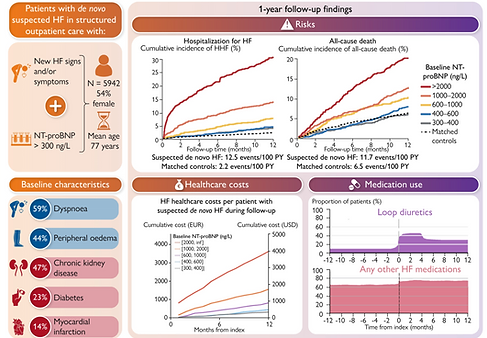
Suspected de novo heart failure The REVOLUTION HF Study
This RWE study showed that patients presenting in outpatient care with suspected de novo HF—defined by new HF signs or symptoms and elevated NT-proBNP—face an immediate and very high risk of HF hospitalization and death. Risks were highest in the first weeks after presentation, underscoring the need for rapid identification, evaluation, and initiation of HF therapy.